The Dominatrix’s Laboratory: Medical Play and the Erotics of Examination
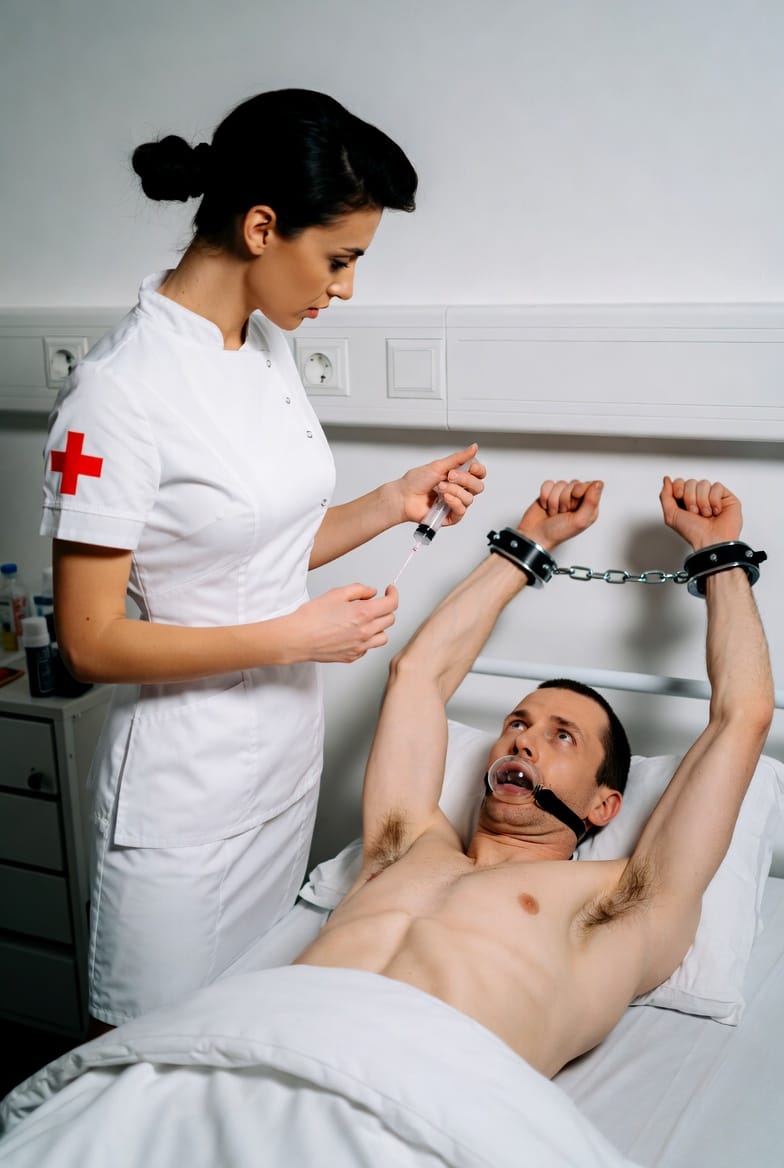
Medical play is a potent BDSM practice that eroticizes clinical power dynamics, blending medical authority with dominance and submission.Its roots trace to Victorian hysteria treatments, Nazi medical experiments, and early 20th-century medical practices, infusing historical trauma and taboo into modern fetishism.The psychology of medical play centers on vulnerability, trust, and the thrill of surrender within a clinical setting, amplifying power exchange and sensory immersion.Techniques range from "check-ups" and enemas to advanced catheterization and electric play, each requiring rigorous safety, hygiene, and consent protocols.Medical play is a profound exploration of control and intimacy, especially in Female Supremacy and Female-Led Relationships (FLRs), fostering trust, catharsis, and emotional connection.
Introduction: The Clinic as Dungeon
The sterile glow of a medical exam room, the cold touch of latex gloves, the sharp scent of antiseptic—these elements evoke a unique blend of fear, submission, and arousal. Medical play, a specialized form of BDSM roleplay, transforms the clinical environment into a dungeon of erotic power exchange. Here, the Dominatrix dons the lab coat, embodying the authority of a doctor or nurse, while the submissive becomes the patient, a body subjected to examination, treatment, and control. This dynamic is far more than simple roleplay; it is a ritualized surrender that merges the language of medicine with the raw power dynamics of dominance and submission.
Medical play is one of the most psychologically potent forms of BDSM, combining the clinical precision of medical procedures with the raw power dynamics of dominance and submission. The Dominatrix, in her lab coat, becomes more than a mistress—she is the authority figure, the healer, the scientist, and the tormentor, all at once. The submissive, stripped of autonomy, becomes the patient, the specimen, the subject—a body to be studied, manipulated, and controlled.
This report explores the historical roots, psychological dynamics, techniques, safety considerations, and cultural implications of medical play, with a particular focus on its role in Female Supremacy and Female-Led Relationships (FLRs). It synthesizes academic research, historical analysis, and contemporary BDSM practices to provide a comprehensive understanding of why medical play is such a compelling and complex form of erotic power exchange.
Historical Roots: From Victorian Hysteria to Nazi Atrocities
Medical fetishism is deeply rooted in historical medical practices that were often invasive, controlling, and imbued with power imbalances. Understanding this history illuminates why medical play resonates so powerfully today.
Victorian Hysteria and the Birth of Medical Fetishism
In the 19th century, female hysteria was a pervasive medical diagnosis, encompassing symptoms such as anxiety, sexual desire, and physical discomfort. The primary treatment was manual genital stimulation to induce "hysterical paroxysm" (orgasm), often performed by physicians. This clinical approach to female sexuality created an early association between medical authority and sexual submission.
- The invention of the vibrator in the late 1880s as a medical device for treating hysteria underscores the clinical origins of sexual stimulation.
- The doctor-patient relationship was inherently unequal, with the physician holding complete control over the patient’s body and treatment.
- This dynamic laid the groundwork for the eroticization of medical authority and the patient’s vulnerability, themes central to modern medical playresearchgate.net+3.
Nazi Medical Experiments: The Darkest Side of Medical Power
During World War II, Nazi physicians conducted horrific experiments on prisoners without consent, often under the guise of medical research. These experiments were part of a broader eugenics and racial hygiene program, involving mass sterilization and torture.
- The experiments included surgical procedures, injections, and other invasive treatments, all conducted in a clinical setting.
- The ethical violations were profound, leading to the Nuremberg Code, which established principles of voluntary consent and ethical medical experimentation.
- While not a fetish in itself, the historical reality of medical authority being used for control and violence has influenced the taboo and transgressive appeal of medical playencyclopedia.ushmm.org+2.
Early 20th Century: The Shift from Physical to Psychological Medicine
The early 20th century saw a shift from physical treatments of hysteria to psychological approaches, including psychoanalysis. This transition reflected changing attitudes toward female sexuality and mental health but also preserved the power imbalance inherent in the doctor-patient relationship.
- The medical profession’s authority remained unchallenged, even as treatments became less physically invasive.
- The clinical setting continued to be a space of control and vulnerability, themes that medical play explores and eroticizespubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+1.
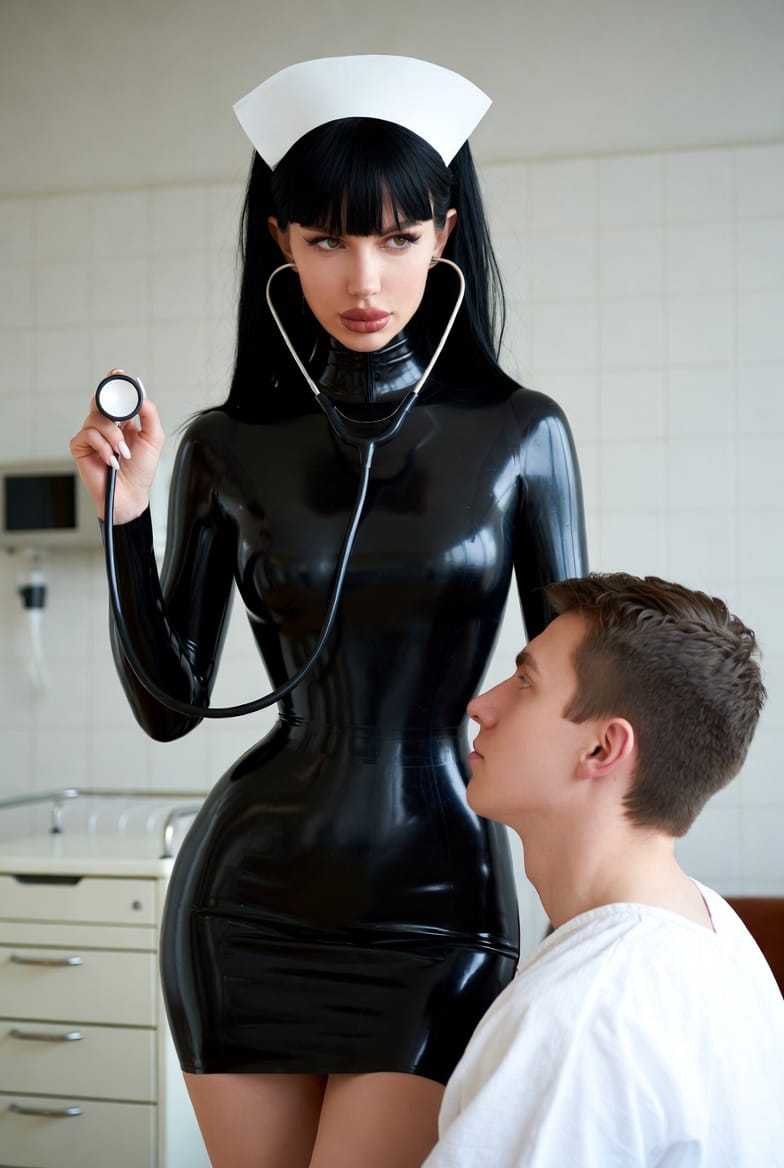

The Psychology of the "Patient" Role: Vulnerability, Trust, and Surrender
Medical play’s psychological power lies in its ability to amplify real-life doctor-patient dynamics within a consensual BDSM framework. The submissive’s role as "patient" involves deep vulnerability, trust, and the thrill of surrender.
Power Exchange and Vulnerability
- The doctor-patient relationship is inherently asymmetrical: one holds authority and expertise, the other is vulnerable and dependent.
- This asymmetry creates a potent psychological dynamic of control and submission, where the submissive experiences helplessness and trust.
- The clinical setting intensifies this dynamic through sensory immersion—latex gloves, cold instruments, medical smells—heightening arousal and anticipationvenomoussin.com+2.
Regression and Comfort
- The "patient" role often involves regression into a childlike or vulnerable state, enhancing the submissive’s sense of dependency.
- The dominant partner, as caregiver, finds pleasure in providing structure and care, creating a nurturing yet controlling dynamic.
- This interplay of vulnerability and care deepens intimacy and trust between partnersuberkinky.com+1.
Sensory and Psychological Immersion
- Medical play engages multiple senses: the smell of antiseptic, the touch of latex, the sound of medical equipment.
- This sensory immersion enhances the psychological experience, blurring the line between real medical procedures and erotic roleplay.
- The clinical detachment of the setting adds a layer of psychological thrill, combining fear and arousalvenomoussin.com+1.
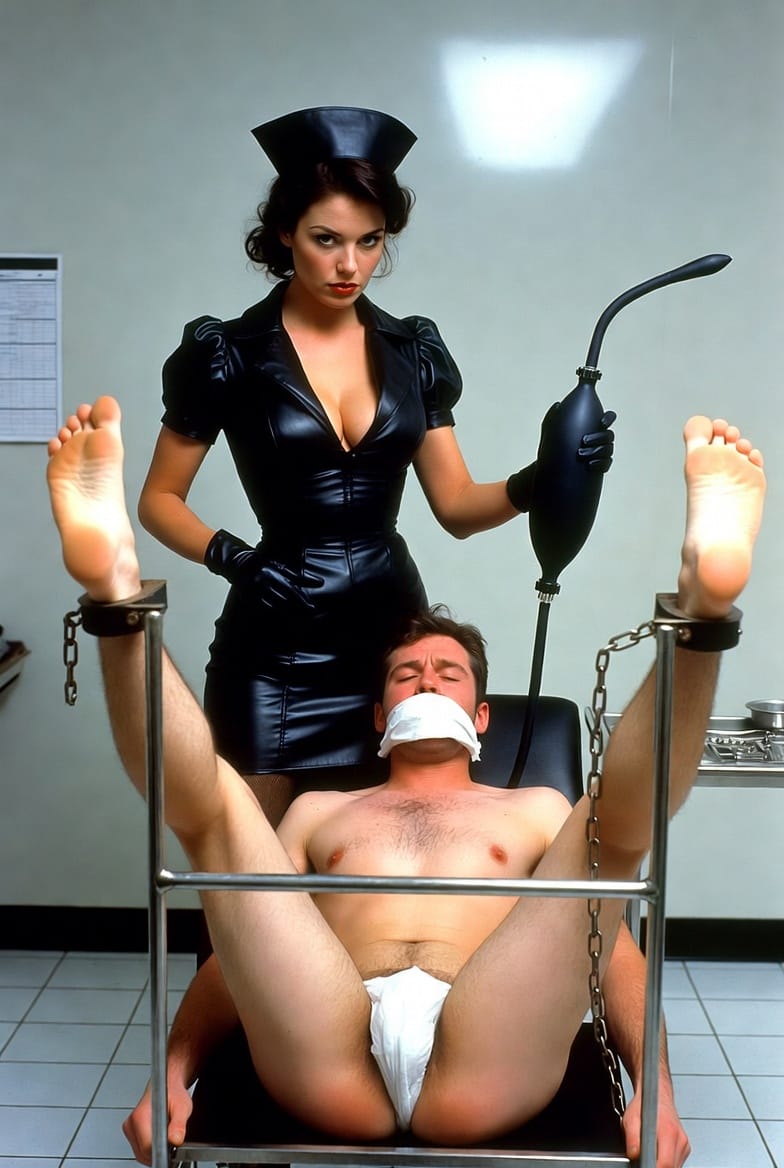
Techniques of the Dominatrix’s Laboratory
Medical play encompasses a spectrum of techniques, from mild roleplay to advanced, invasive procedures. Each technique carries specific risks and requires strict safety protocols.
The "Check-Up": Examination and Humiliation
- The scene begins with the submissive as patient, subjected to a full-body inspection.
- Includes strip-and-weigh-in, reflex tests, oral and genital exams, and rectal temperature-taking.
- The Dominatrix uses medical props (stethoscope, gloves, speculum) to enhance realism and power exchange.
- Psychological play includes humiliation, objectification, and forced complianceprogressivetherapeutic.com.au+1.
Enemas: Cleansing and Control
- Enemas involve inserting fluid into the rectum, creating sensations of fullness, pressure, and vulnerability.
- Can be used for humiliation, discipline, or sensory play.
- Safety requires body-temperature water, lubrication, and never using soap or harsh chemicals.
- Enema play symbolizes purification and control, enhancing the submissive’s sense of surrenderprogressivetherapeutic.com.au+2.
Catheters: Urethral Penetration and Bladder Control
- Catheterization is an advanced technique involving insertion of a tube into the urethra.
- Used for bladder control, forced hydration, or prostate stimulation.
- Carries high risk of infection and injury; requires sterile technique and medical knowledge.
- Often combined with medical restraints and gags for heightened realismbondesque.com+1.
Saline Injections and IV Drips (Simulated)
- Simulated injections and IV drips use needles or butterfly needles for sensory play.
- Real injections are dangerous; only trained professionals should administer them.
- Roleplay includes "treatments" for dehydration or illness, adding a layer of medical realisminkaklinic.com.
Electric Play: "Defibrillation" and Sensory Stimulation
- Uses TENS units or violet wands to deliver electrical currents to the body.
- Creates sensations ranging from tingling to pain, depending on intensity.
- Must avoid sensitive areas (heart, genitals without caution) and start on low settings.
- Adds a technological and clinical edge to medical playinkaklinic.com.
Sounding: Urethral Penetration with Rods
- Involves inserting thin rods into the urethra for intense sensory stimulation.
- Requires sterile, body-safe materials and careful technique to avoid injury.
- Often part of advanced medical play, symbolizing deep submission and controlbondesque.com+1.
"Forced Treatment": Simulated Medical Procedures
- Includes suturing, stapling, wound care, and other medical interventions.
- Requires extensive knowledge and safety precautions due to risk of injury.
- Used to simulate surgical or emergency scenarios, intensifying the power dynamicinkaklinic.com.
Safety, Ethics, and Best Practices
Medical play carries significant risks, making safety, consent, and aftercare essential.
Consent and Negotiation
- All participants must fully consent to activities, discussing boundaries, safe words, and medical history.
- Pre-scene negotiation covers comfort levels with props, roleplay, and physical contact.
- During the scene, check-ins ensure ongoing consent and comfortvenomoussin.com+1.
Hygiene and Sterilization
- All equipment must be sterilized or disposable to prevent infection.
- Latex gloves, speculums, needles, and catheters require rigorous cleaning protocols.
- Proper lubrication and gentle handling reduce risk of injuryvenomoussin.com+1.
Aftercare
- Post-scene aftercare includes physical care (cleaning, bandaging) and emotional support.
- Participants may experience emotional drop or vulnerability after intense play.
- Open communication and reassurance are crucialconsentculture.community.
Ethical Considerations
- Medical play must respect participants’ dignity and boundaries.
- Avoid triggering real medical trauma or PTSD.
- Adhere to ethical principles of care, respect, and informed consentcdc.gov+2.
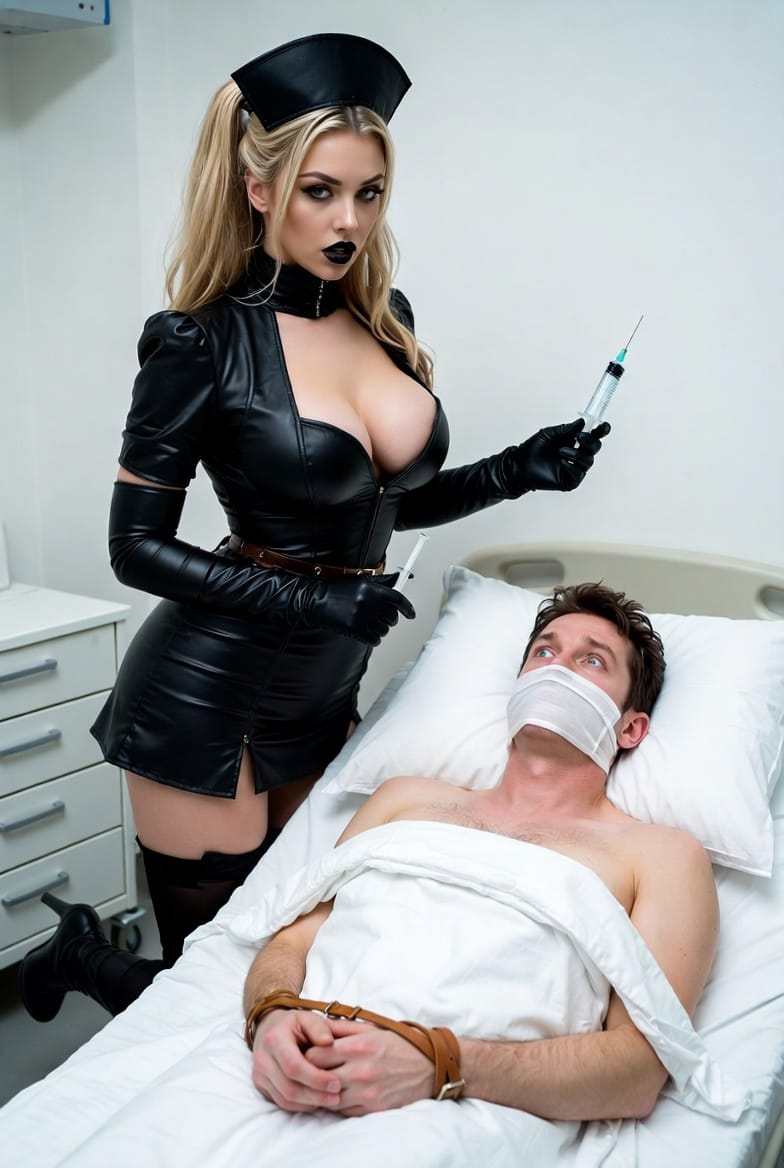

Medical Play in Female Supremacy and Female-Led Relationships (FLRs)
Medical play is particularly potent in Female Supremacy and FLRs, where the dominant woman embodies medical authority.
Power Exchange and Trust
- The Domme takes on the role of doctor or nurse, exerting control and care.
- The submissive male or partner plays the patient, surrendering to her authority.
- This dynamic enhances trust, intimacy, and emotional connectionen.wikipedia.org+1.
Psychological and Emotional Rewards
- Medical play allows partners to explore vulnerability, control, and intimacy in a safe, consensual space.
- It can be cathartic, helping process anxieties related to real medical experiences.
- Strengthens communication, mutual respect, and emotional bondingen.wikipedia.org+1.
Safety and Communication
- FLRs emphasize clear boundaries, negotiation, and aftercare.
- Medical play within FLRs requires open dialogue about desires, limits, and emotional needsdiversity.social+1.
Cultural and Societal Implications
Medical play reflects and influences broader cultural attitudes toward medicine, power, and sexuality.
Medical Dramas and Public Perception
- Medical dramas shape societal views of healthcare, illness, and doctor-patient relationships.
- They humanize illness, making medical experiences relatable and understandable.
- Influence public sentiment and medical ethics trainingpublishing.mediamutations.org+1.
Media Representation and Fetishization
- Medical fetishism is represented in pornography and erotic literature, often focusing on uniforms, instruments, and power dynamics.
- Media narratives reflect societal ideas about gender, power, and medical authority.
- The fetishization of medical roles and equipment is a common theme in BDSM cultureen.wikipedia.org+1.
Ethical and Educational Impact
- Medical play can be a tool for education and social inclusion, fostering empathy and understanding.
- It raises awareness about consent, safety, and the ethical boundaries of medical practice.
- Encourages critical reflection on power dynamics and vulnerability in healthcare settingsbmcmededuc.biomedcentral.com+1.
Summary Table: Key Medical Play Techniques and Safety Considerations
| Technique | Description | Risks | Safety Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Check-Up | Physical exam, reflex tests, oral/genital inspection | Psychological humiliation, discomfort | Consent, safe words, hygiene |
| Enema | Fluid insertion into rectum | Infection, discomfort | Body-temperature water, lubrication, no soap |
| Catheterization | Urethral tube insertion | Infection, injury | Sterile technique, medical knowledge |
| Saline Injection | Simulated IV or injections | Infection, injury | Only simulated or by trained professionals |
| Electric Play | Electrical stimulation (TENS, violet wand) | Burns, nerve damage | Avoid heart/genitals, start low, monitor use |
| Sounding | Urethral rod insertion | Infection, injury | Sterile, body-safe materials, careful technique |
| Forced Treatment | Simulated sutures, wound care | Infection, injury | Medical knowledge, sterile equipment |
Conclusion
The Dominatrix’s Laboratory is a complex, multifaceted realm where medical authority meets erotic power exchange. Rooted in historical medical practices and psychological dynamics of vulnerability and trust, medical play offers a unique space for exploring submission, control, and intimacy. Techniques range from simple examinations to advanced, invasive procedures, all requiring rigorous safety and ethical considerations.
Within Female Supremacy and Female-Led Relationships, medical play becomes a powerful tool for fostering trust, intimacy, and emotional connection. It allows partners to explore vulnerability and control in a safe, consensual environment, deepening their bond through shared experiences of power exchange.
Culturally, medical play reflects and influences societal attitudes toward medicine, power, and sexuality, shaping public perceptions through media representation and educational narratives. It serves as both a form of erotic expression and a tool for fostering empathy and understanding about medical experiences.
The Dominatrix’s Laboratory, therefore, is not merely a dungeon of clinical fetishism but a profound exploration of power, vulnerability, and intimacy—bridging the gap between medical authority and erotic submission.





